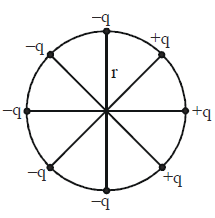
Solution:
Electric Potential (\( V \)):
1. Potential at the center due to a charge \( q \) at a distance \( r \) is:
\[
V = \frac{kq}{r}.
\]
2. Total potential is the algebraic sum since potential is scalar. For 3 positive charges and 5 negative charges:
\[
V_{\text{total}} = 3 \cdot \frac{kq}{r} - 5 \cdot \frac{kq}{r} = \frac{-2kq}{r}.
\]
---
Electric Field (\( E \)):
1. Symmetry of arrangement: The charges along the diagonals cancel their horizontal components, leaving only vertical components.
2. Field due to charges along diagonals (\( -q, -q, +q, +q \)):
- Each diagonal pair creates a net field of magnitude:
\[
E_{\text{pair}} = \frac{\sqrt{2}kq}{r^2}.
\]
- Two such pairs contribute:
\[
E_{\text{diagonals}} = 2 \cdot \frac{\sqrt{2}kq}{r^2} = \frac{2\sqrt{2}kq}{r^2}.
\]
3. Field due to the remaining vertical pair (\( -q, -q \)):
- Net field:
\[
E_{\text{vertical}} = \frac{2kq}{r^2}.
\]
4. Total electric field:
\[
E_{\text{total}} = E_{\text{diagonals}} + E_{\text{vertical}} = \frac{2kq}{r^2}(1 + \sqrt{2}).
\]
---
Final Answer:
\[
E = \frac{2kq}{r^2}(1 + \sqrt{2}), \quad V = \frac{-2kq}{r}.
\]
Leave a Reply